Making Choices
Overview
Teaching: 20 min
Exercises: 20 minQuestions
How can my programs do different things based on data values?
Objectives
Write conditional statements including
if,elif, andelsebranches.Correctly evaluate expressions containing
andandor.
A key part of programming is making the computer do different things depending on the outcome
of a test. This functionality is provided by the conditional statements if, elif, and else.
Conditionals
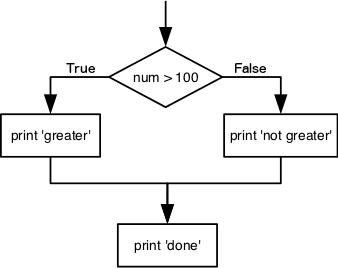
We can ask Python to take different actions, depending on a condition, with an if statement:
num = 37
if num > 100:
print('greater')
else:
print('not greater')
print('done')
not greater
done
The second line of this code uses the keyword if to tell Python that we want to make a choice.
If the test that follows the if statement is true,
the body of the if
(i.e., the lines indented underneath it) are executed.
If the test is false,
the body of the else is executed instead.
Only one or the other is ever executed:
Conditional statements don’t have to include an else.
If there isn’t one,
Python simply does nothing if the test is false:
num = 53
print('before conditional...')
if num > 100:
print(num,' is greater than 100')
print('...after conditional')
before conditional...
...after conditional
We can also chain several tests together using elif,
which is short for “else if”.
The following Python code uses elif to print the sign of a number.
num = -3
if num > 0:
print(num, 'is positive')
elif num == 0:
print(num, 'is zero')
else:
print(num, 'is negative')
"-3 is negative"
Note that to test for equality we use a double equals sign ==
rather than a single equals sign = which is used to assign values.
That’s Not Not What I Meant
Sometimes it is useful to check whether some condition is not true. The Boolean operator
notcan do this explicitly.if not (a < b): print('a is NOT less than b') if not c == d: print('c is NOT equal to d')
We can also combine tests using and and or.
and is only true if both parts are true:
if (1 > 0) and (-1 > 0):
print('both parts are true')
else:
print('at least one part is false')
at least one part is false
while or is true if at least one part is true:
if (1 < 0) or (-1 < 0):
print('at least one test is true')
at least one test is true
What Is Truth?
TrueandFalseare special words in Python calledbooleans, which represent truth values. A statement such as1 < 0returns the valueFalse, while-1 < 0returns the valueTrue. However, theseTrueandFalsebooleans are not the only values in Python that are true and false. In fact, any value can be used in aniforelif. The code below shows how some of these conditionals work:if 'word': print('word is true') if not '': print('empty string is NOT true') if [1, 2, 3]: print('non-empty list is true') if not []: print('empty list is NOT true') if 1: print('one is true') if not 0: print('zero is NOT true')
You can also perform special tests against lists and dictionaries to see if an object is contained
in them by using in. For lists, this is simply if the object is in the list. For dictionaries,
it checks if the value is in the list of keys, not values.
my_list = ["apple", "orange", "pear"]
if "pear" in my_list:
print("I've found a pear!")
I've found a pear!
How Many Paths?
Consider this code:
if 4 > 5: print('A') elif 4 == 5: print('B') elif 4 < 5: print('C')Which of the following would be printed if you were to run this code? Why did you pick this answer?
- A
- B
- C
- B and C
Solution
C gets printed because the first two conditions,
4 > 5and4 == 5, are not true, but4 < 5is true.
Close Enough
Write some conditions that print
Trueif the variableais within 10% of the variablebandFalseotherwise. Hint: You can make the condition easier to understand if you use theabsfunction —helpwill tell you what it does!Solution 1
a = 5 b = 5.1 if abs(a - b) < 0.1 * abs(b): print('True') else: print('False')Solution 2
print(abs(a - b) < 0.1 * abs(b))This works because the Booleans
TrueandFalsehave string representations which can be printed.
Key Points
Use
if conditionto start a conditional statement,elif conditionto provide additional tests, andelseto provide a default.The bodies of the branches of conditional statements must be indented.
Use
==to test for equality.
X and Yis only true if bothXandYare true.
X or Yis true if eitherXorY, or both, are true.Zero, the empty string, and the empty list are considered false; all other numbers, strings, and lists are considered true.
TrueandFalserepresent truth values.